
Introduction
Blockchain technology has emerged as one of the most groundbreaking innovations of the 21st century. Its decentralized, transparent, and secure framework is being adopted in various sectors, from finance and healthcare to supply chain management and beyond. But what exactly is blockchain, and why is it so transformative?
In this guide, we’ll break down blockchain technology in simple terms, explore its real-world applications, and discuss what the future holds. By the end, you’ll have a solid understanding of blockchain and why it’s a buzzword in today’s tech-driven world.
1. What is Blockchain Technology?
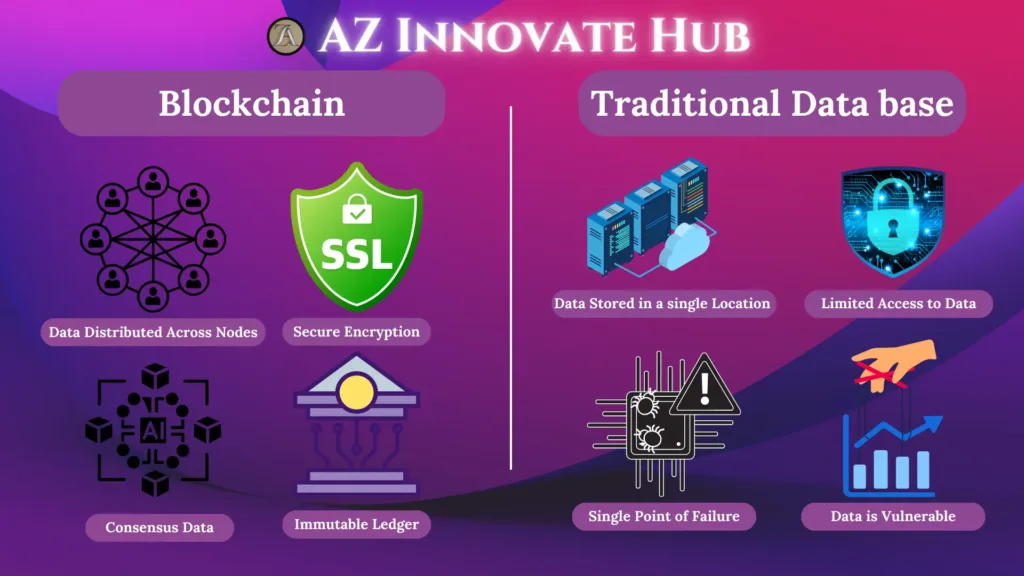
Blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology (DLT) that records transactions in a decentralized, secure, and transparent manner. Think of it as a digital ledger where every transaction is recorded as a “block,” and each block is linked or “chained” to the previous one. This chain of blocks forms a database that’s immutable and shared across multiple nodes (computers) in the network.
Real-World Example: Imagine a Google Doc that’s shares with a group of people. Everyone in the group has access to the same document simultaneously, and any changes are visible to all members. This decentralized nature ensures transparency and prevents unauthorized alterations.
2. How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network, which means there’s no central authority or intermediary, like a bank, controlling the transactions. When a transaction is initiated, it’s broadcast to all the nodes in the network. Once verified, it’s grouped into a new block, which is then added to the chain permanently.
Key Terms to Know:
- Nodes: Independent computers that maintain a copy of the entire blockchain.
- Hash: A unique code representing the transaction data in the block.
- Consensus Mechanism: A protocol used by nodes to agree on the validity of transactions. Common mechanism include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
3. Benefits of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain’s unique attributes offer several benefits:
- Transparency: Every transaction is visible to participants, ensuring accountability.
- Security: Transactions are encrypted, and once recorded, data cannot be altered without consensus from the network.
- Decentralization: No single entity has control, reducing the risk of fraud or manipulation.
Real-World Example: Walmart uses blockchain to track the journey of food products from farm to store, ensuring transparency in the supply chain. This helps in tracing contaminated food sources quickly, enhancing consumer safety.
4. Blockchain Applications Across Industries
- Finance: Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum operate on blockchain, offering a decentralized form of money transfer and investment.
- Healthcare: Blockchain can securely store patient records, allowing authorized medical personnel to access data efficiently.
- Supply Chain Management: Companies like IBM are using blockchain to track product provenance and reduce counterfeiting.
5. Understanding Cryptocurrencies and Smart Contracts
One of the most popular applications of blockchain is cryptocurrencies. Bitcoin, launched in 2009, was the first digital currency to use blockchain technology. Cryptocurrencies use blockchain to enable secure peer-to-peer transactions without the need for banks.
Another notable application is smart contracts – self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. For example, in real estate, a smart contract can automate payments and transfer ownership once the buyer fulfills their end of the deal.
6. Challenges of Blockchain Adoption
Despite its benefits, blockchain faces several challenges:
- Scalability: Handling a high volume of transactions can slow down the network.
- Regulatory Issues: Lack of regulatory clarity in many countries hinders adoption.
- Energy Consumption: Proof of Work-based blockchains like bitcoin consume enormous energy.
7. How to use Blockchain Technology?
Using blockchain is simpler than you might think. If you want to transfer money using a cryptocurrency like Bitcoin, you can:
- Create a Digital Wallet: Download a wallet app like Coinbase or Trust Wallet.
- Buy Cryptocurrency: Purchase Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies using traditional currency.
- Send/Receive Money: Use the wallet address to send or receive funds with anyone, anywhere, without a bank.
Pro Tip: Blockchain-based platforms like Ethereum also allow you to create and deploy smart contracts, which automate transactions without intermediaries.
8. Future of Blockchain: What's Next?
Blockchain technology is still in its early stages, but its potential is immense. Future advancements could include:
- Interoperability: Enabling different blockchain networks to communicate and exchange data seamlessly.
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Expanding financial services like lending, borrowing, and insurance on blockchain platforms.
- Integration with AI and IoT: Combining blockchain with Artificial Intelligence and the Internet of Things for enhanced data management and security.
Real-World Example: In 2023, the Bank of England explored using blockchain for a digital pound, potentially revolutionizing how national currencies are managed.
9. Why Should You Care About Blockchain?
Blockchain isn’t just for tech enthusiasts or financial professionals. It’s a technology that’s impacting the daily lives of people and could change how we transact, own assets, and interact with the digital world. By understanding blockchain now, you’ll be ahead of the curve as more industries integrate this transformative technology.
10. Getting Started with Blockchain: Resources and Learning
To dive deeper into blockchain, here are a few resources:
Final Thoughts
Blockchain technology is more than just a buzzword. It’s a powerful tool with the potential to transform industries and improve our lives. By understanding the basics now, you’ll be prepared for a future where blockchain is as common as the internet.
