
Network Traffic Monitoring: Understanding IDS and Its Role in Detecting Potential Cyber Attacks
Cyber threats are getting more complex, and our network security needs to keep up. An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is a key tool in this fight. It watches network traffic for signs of trouble, like suspicious activities or attacks.
IDS uses two main methods to spot threats: looking for known patterns and finding unusual behavior. This way, it can alert us in real-time when finds something wrong. Adding IDS to our security plans helps us see what’s happening on our networks better. It also lets us act fast when we find a problem, keeping our data safe.
As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, knowing how IDS works is crucial. It helps us keep our networks strong and secure against all kinds of attacks.
Key Takeaways
- An Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) monitors network traffic for suspicious activity.
- Types of IDS include network-Based (NIDS) and Host-Based (HIDS) detection systems.
- Signature-based and anomaly-based detection methods enable effective cyber attach detection.
- It’s essential to integrate IDS with other security tools like firewalls and IPS for enhanced protection.
- Maintaining an effective IDS requires fine-tuning to mitigate false positives and false negatives.
- Employing machine learning in IDS can improve threat identification and incident response capabilities.
Introduction to Network Monitoring and Security
In today’s digital world, network monitoring is key to protecting our systems. It watches over network traffic to spot and stop bad activities. This makes a safe space for everyone and businesses.
A big part of our security plan is using IDS. These systems quietly watch network data without stopping it. They look for known threats and alert us when they find something bad.
We also use many cybersecurity tools to get better at defending ourselves. Tools like Zabbix and Snort help us watch our network and keep it running well. They also help us follow security rules. Putting IDS behind firewalls helps us see more of what’s coming in, making us better at finding threats.
As cyber threats get more complex, we need to stay ahead by monitoring more. Using IDS helps us find threats fast and improve our security plans. Good monitoring is crucial for spotting and fixing risks to our network.
Importance of Monitoring Network Traffic
In today’s world, watching traffic key to he to keeping our systems safe. We use advanced tools to fight off cyber threats. This is especially true for stopping unauthorized access and finding malware.
Threats in Modern Networks
Cyber attackers use new tricks to get into our networks. IDS help by spotting possible threats. They send alerts so we can act fast when trouble starts.
IDS can find known threats and unknown dangers in our traffic. This means we can keep our networks safe all the time. We learn about attacks and can lower the chance of data leads. Using these tools helps us see threats better and follow rules, we can fight off unauthorized access and stay ahead of hackers.
What is an Intrusion Detection System (IDS)?
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is key to our network security. It watches traffic for signs of trouble and checks for known threats. It alerts us to potential dangers, helping us act fast. By identifying vulnerabilities and anomalies, IDS enables proactive measures to strengthen our defenses. Additionally, IDS provides valuable insights into attack patterns and trends, informing our incident response strategies. Ultimately, IDS plays a critical role in safeguarding our sensitive data and maintaining the integrity of our network infrastructure.
Definition and Overview
An IDS is a security tool that checks both incoming and outgoing network traffic. It looks for odd behavior and threats. This helps keep our data safe from cyberattacks.
By continuously monitoring network activity, an IDS identifies potential security breaches and alerts administrators to take swift action. It detects various types of malicious activities, including hacking attempts, malware, and denial-of-service attacks.
Types of IDS: Network-Based vs. Host-Based
IDS can be categorized into two primary types: Network-Based IDS (NIDS) and Host-Based IDS (HIDS). Each has distinct strengths and monitoring approaches.
Network-Based IDS (NIDS):
- Monitors entire network segments
- Analyzes traffic patterns to identify potential security threats
- Inspects packet headers and contents
- Detects malicious traffic, denial-of-service attacks, and policy violations
- Typically deployed at network chokepoints (e.g. routers, switches)
Host-Based IDS (HIDS):
- Focuses on individual hosts (servers, workstations, devices)
- Analyzes system logs, file integrity, and process activity
- Detects local threats, unauthorized access, and malware
- Monitors system configuration changes and file modifications
- Often integrated with host-based firewalls and antivirus software
Hybrid IDS:
- Combines NIDS and HIDS capabilities
- Provides comprehensive visibility into network and host activity
- Offers enhanced detection and response capabilities
Other Variants:
- Distributed IDS (DIDS): Multiple sensors coordinated to monitor large networks
- Protocol-Based IDS (PIDS): Focuses on specific protocols (e.g. HTTP, FTP)
- Application-Based IDS (AIDS): Monitors application-layer traffic
Understanding the differences between NIDS, HIDS, and hybrid approaches helps organizations choose the best IDS strategy for their unique security needs.
Passive Monitoring in IDS
Passive monitoring is a key part of IDS. It lets the system watch network behavior without showing it down. This helps us spot odd behavior and unknown threats.
While IDS alerts us in real-time, managing these alerts can be tough. We have to deal with too many alerts and false positives. Knowing these issues helps us improve our security without slowing down our work.

How IDS Detects Possible Attacks
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) use different ways to spot threats in network traffic. They use signature-based and anomaly-based detection to help prevent cyber-attacks. Let’s dive into these methods.
Signature-Based Detection
Signature-Based Detection is a key part of IDS. It checks network traffic against a list of known attack patterns. When it finds a match, it sends out an alert. This method works well for known threats but can miss new, unknown attacks. Recent data shows that signature-based systems often miss complex attacks. This shows we need more than one way to protect our networks.
Furthermore, signature-based detection relies on regularly updated signature databases to stay effective. Outdated signatures can leave networks vulnerable to newly emerging threats. Additionally, sophisticated attackers often modify known exploits to evade signature-based detection. Therefore, combining signature-based detection with behavioral and anomaly-based detection methods is crucial for comprehensive network security.
Anomaly-Based Detection
Anomaly-based detection looks for unusual patterns in network activity. It sets a baseline of normal behavior and alerts for anything out of the ordinary. This method can catch unknown threats, including those without a known signature. As cyber threats grow, using anomaly-based detection helps us stay ahead. It lets us tackle new risk before they become big problems.
By continuously learning and adapting to network traffic patterns, anomaly-based detection improves it accuracy over time. This proactive approach enables security teams to respond swiftly to emerging threats. Moreover, anomaly-based detection complements signature-based detection, enhancing overall network security posture. By identifying deviations from normal behavior, it provides valuable insights into potential vulnerabilities and helps mitigate zero-day attacks.
Behavioral Monitoring
Behavioral monitoring watches how users and networks behave. It looks for any odd behavior that doesn’t fit the norm. By combining this with other IDS methods, we get a clearer view of our networks.
This helps us stop both outside attacks and insider threats. Mixing behavioral analysis with other detection methods helps us face the changing threat world.

Benefits of Using IDS in Network Security
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) bring big benefits to network security. They help us manage threats before they happen. IDS gives us real-time alerts, so we can act fast to stop damage.
These systems help us detect threats quickly. They also teach us about the best ways to protect our networks.
Real-Time Alerts
IDS are great because they send alerts right away when they spot something suspicious. They watch network traffic all the time. This helps our teams deal with threats fast.
Spotting threats early helps us avoid big problems. It keeps our networks safe from unauthorized access.
Low Resource Utilization
IDS are also good because they don’t use up a lot of resources. They watch traffic without slowing down our network. Modern IDS don’t slow things down like old systems did.
This means our network stays fast and secure. We get the security we need without losing speed.
Enhanced Threat Visibility
IDS also help us see threats more clearly. They show us what’s happening in our network. This lets us find and fix weak spots.
We can see both outside and inside threats. This helps us fix problems before they get worse. We stay on top of our security by keeping our systems updated.
Using IDS well makes our networks stronger against cyber threats. By following these steps, we keep our networks safe and up to date.
Challenges and Limitations of IDS
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) help protect us by spotting potential threats. But they face several challenges that can make them less effective. Complex network architecture sand high traffic volumes can overwhelm IDS capabilities, leading to false positives or missed detections. Furthermore, rapidly evolving threat landscapes and sophisticated attack tactics require constant IDS updates and fine-tuning to maintain optimal performance.
False Positives and Negatives
IDS often deal with false positives and negatives. False positives can flood teams with useless alerts, taking away from real threats. False Negatives let actual attacks slip by, causing big security problems.
Signature-based IDS are good at catching known threats but miss new ones. Anomaly-based systems can spot unusual behavior but might flag too many things as threats.
Limited Response Capabilities
IDS also have a big limitation: they can’t act fast. They mainly alert teams, not fix problems right away. This can slow down our response, especially when time is critical.
The number of alert can overwhelm us, making it hard to focus on real threats.
Overcoming IDS Challenges
To beat these challenges, we need to improve our detection methods and how we handle alerts. We need skilled teams and procedures to manage alerts without disrupting work. Using IDS with tools like SIEM can give us a better view of threats, helping us respond faster.
Furthermore, Implementing advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms enhances IDS accuracy and reduces false positives. Integrating IDS with other security tools, such as firewalls and antivirus software, creates a robust defense-in-depth strategy. By prioritizing alert validation and incident response planning, organizations can maximize IDS effectiveness and minimize potential security breaches.
Role of IDS in the Broader Security Ecosystem
In today’s complex cybersecurity world, knowing about Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) is key. We must understand the difference between IDS and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) to protect well. IDS watches for suspicious activities without interfering, while IPS blocks threats actively. It’s also vital to link IDS with firewalls, as firewalls filter traffic and IDS spots security breaches.
IDS vs. IPS: Key Differences
Looking at IDS vs. IPS, we see IDS is passive and watches network traffic without slowing it down. IPS, on the other hand, works actively to stop threats in real-time. This shows why using both systems is crucial for strong security. IDS uses real-time monitoring and different detection methods to track threats.
While anomaly-based detection catches new threats well, it often finds false positives. Signature-based detection is better at spotting known threats.
Integrating IDS with Firewalls and SIEM
Linking IDS with firewalls boosts an organization’s security. Firewalls block unwanted traffic, and IDS gives deeper insight into possible breaches. Also, connecting IDS data with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) helps in responding to incidents. This way, organization can better understand threats by correlating events.
Ansible Automation Platform makes this integration easier by managing various security tools, like IDS and SIEM. This leads to faster and more effective responses to threats. By updating IDPS rules automatically, we can detect and handle new threats better.
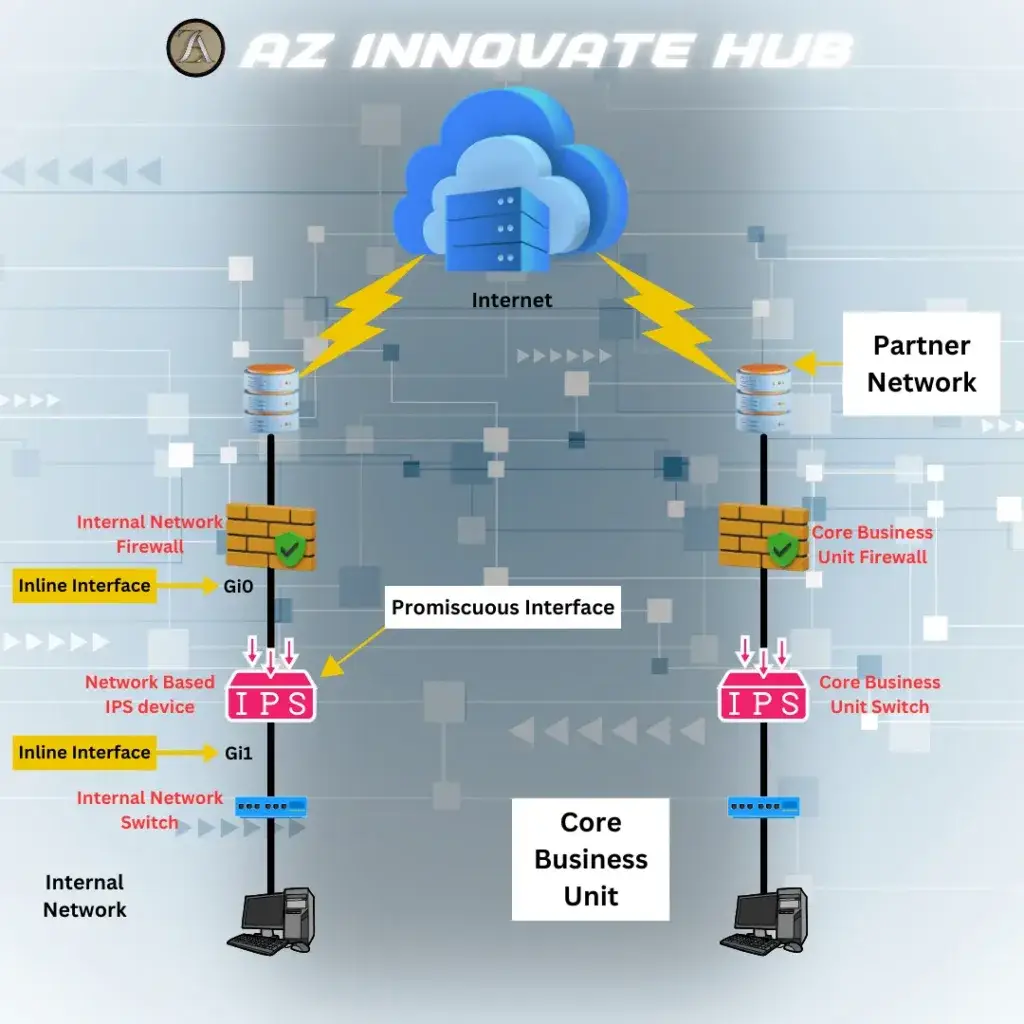
Future of IDS in Cybersecurity
The world of cybersecurity is changing fast, thanks to new threats. AI-powered IDS solutions are leading the way, making threat detection better. They use machine learning to quickly analyze lots of data, keeping up with new threats.
As threats get smarter, using advanced analytics in IDS is key. This helps detect intrusions more effectively.
AI-Powered IDS Solutions
Artificial Intelligence and machine learning are changing IDS. They help spot unusual network behavior, catching new threats. Cloud-based IDS solutions are also becoming popular, offering flexible security for cloud environments. Modern IDS can even set traps for attackers, known as honeypots. This gives us insights into how they work.
By leveraging AI-driven anomaly detection and predictive analytics, IDS solutions can identify complex threats in real-time. Additionally, AI-powered IDS solutions enable automated incident response, containing breaches before they spread. Furthermore, integration with threat intelligence feeds enhances AI-powered IDS capabilities, staying ahead of emerging threats. As AI technology advances, IDS solutions will become increasingly adept at detecting zero-day attacks and advanced persistent threats.
IDS and the Growing Complexity of Cyber Threats
IDS working with SIEM systems is a big plus. It gives a full view of security, helping with threat tracking and response. To deal with false positives, using both HIDS and NIDS is smart.
IDS is also evolving to watch over IoT devices. This shows how IDS is adapting to new security needs. So, the future of IDS is about staying sharp and adaptable in changing threat world.
Conclusion: The Value of IDS in Today's Network Security Landscape
In today’s fast-changing digital world, IDS are key for keeping networks safe. They watch over network traffic, spotting and stopping cyber threats. This makes our networks safer and helps us respond quickly to attacks.
IDS face challenges like false alarms and needing human help. But their benefits are clear. New tech like AI and machine learning is making them better at finding threats. This helps us meet rules like GDPR and HIPAA, showing we care about keeping data safe.
IDS are essential for a strong cybersecurity plan. They help protect important data and keep it from falling into the wrong hands. As we work to improve threat detection, IDS keep getting better. They help us stay ahead of cyber threats. With careful planning and updates, IDS will keep leading our fight for network security.



