Beyond basic servers and storage, the true power of the cloud lies in managed services. These services handle advanced data management and serverless code execution, allowing you to build powerful applications. This article covers advanced databases and the revolutionary serverless model, headlined by AWS Lambda.
Cloud providers offer fully managed database services, which reduce the client’s maintenance costs. These services handle crucial operational tasks like monitoring, managing, and scaling the database automatically.
Managed Database Services
A database is distinct from simple storage; it includes both storage and processing capabilities.
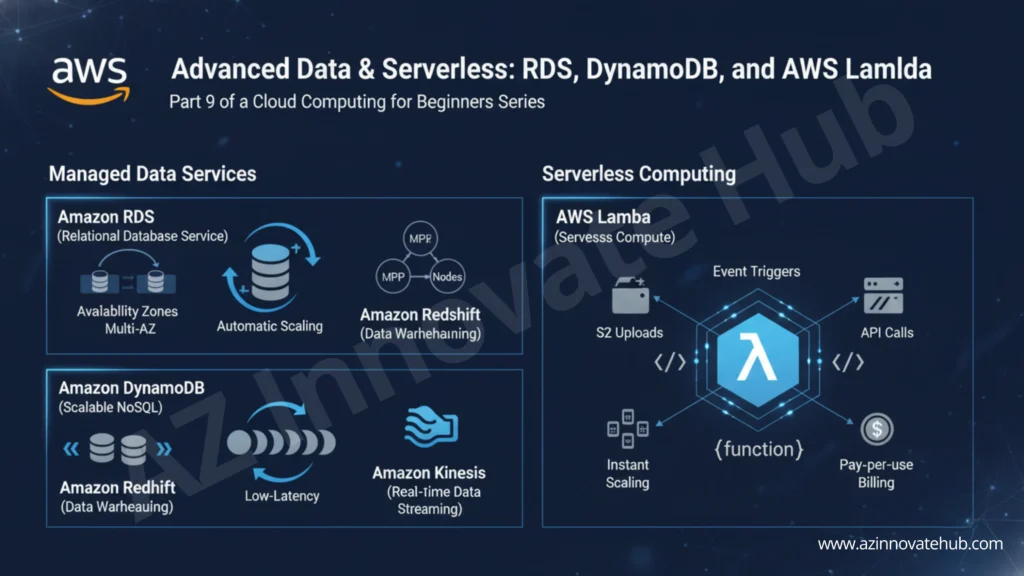
- Relational Databases (RDS) AWS Relational Database Service (RDS) provides managed, relational databases. It supports traditional SQL databases like PostgreSQL, MySQL, and SQL Server.
- High Availability (Multi-AZ): Durability (ensuring data is not lost) and High Availability (ensuring the database is accessible) are the most important concepts for RDS. RDS uses Multi-AZ deployments to achieve this. In this setup, RDS automatically maintains a standby database in a different Availability Zone. If the primary database fails, RDS automatically fails over and redirects requests to the standby database. This provides fault tolerance.
- Storage Scaling: The storage allocated to the database can be scaled automatically up to a defined limit.
- NoSQL Databases are designed to handle large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data with rapid growth or fluctuating demand.
- Amazon DynamoDB: This is fully managed NoSQL database service from AWS, known for being fast and scalable. DynamoDB automatically scales to handle millions of requests per second, making it essential for applications requiring low latency. For example, Lyft switched to DynamoDB to handle millions of real-time ride requests, scaling automatically to meet peak demand.
- Other Providers: Azure provides Cosmos DB, a globally distributed NoSQL database. GCP is noted for its data analytics strengths, particularly BigQuery for high-speed SQL queries.
Data Warehousing and Streaming
- Amazon Redshift: This is a fast, scalable, and fully managed data warehouse. It simplifies data analysis by using standard SQL to run complex analytics queries against petabytes of structured data. Redshift uses Massively Parallel Processing (MPP), where multiple “compute nodes” and “node slices” work in parallel to achieve high performance.
- Amazon Kinesis: This service is used for processing streaming data in real-time. Producers (like mobile clients or EC2 instances) push data into Kinesis Data Streams. Consumers then use a library to process that data as it arrives.
Serverless Computing (FaaS) with AWS Lambda
Serverless computing, or Function as a Service (FaaS), abstracts away the management of servers and operating systems. This allows users to focus solely on their code.
- What is AWS Lambda?
AWS Lambda is the primary FaaS offering in AWS. It is an event-driven execution model that executes your code in response to triggers. A trigger could be an image uploaded to S3 or a request from an API Gateway. - Pay-Per-Use Model: AWS Lambda charges only for the exact compute time used, measured in milliseconds. This model eliminates the need to pay for idle time. One company, iRoot, saw 90% reduction in infrastructure cost by using AWS Lambda.
- Automatic Scaling: AWS Lambda instantly scales up with the number of function calls, making it perfect for fluctuating workloads. iRoot, for example, used AWS Lambda to process over 20 million events per day, scaling effortlessly.
- Other Providers: Other clouds offer similar services. Azure Functions allows developers to create applications in languages like C#, Java, or NodeJS, and GCP offers GCP Cloud Functions.
Conclusion: Moving Beyond Infrastructure
You have now graduated from core infrastructure to advanced, managed platforms. You’ve seen how managed databases like RDS (for SQL) and DynamoDB (for NoSQL) remove the burden of maintenance and provide high availability and massive scale. We also touched on data warehousing with Redshift.
Most importantly, you’ve learned the power of serverless computing with AWS Lambda, a FaaS model that lets you run code without thinking about servers, paying only for what you use.
You now have a comprehensive understanding of what is and what it can do. In our final article, we will provide a complete roadmap for turning this knowledge into a cloud computing career.