Before the cloud, businesses had to rely on traditional on-premises IT setups. Starting a new venture meant purchasing expensive physical servers and hardware, requiring a large initial capital expenditure. Companies spent heavily on hardware, software maintenance, and dedicated IT teams. This approach was inefficient. If a product gained traction, the company had to buy more servers to handle the traffic. If traffic slowed down, those expensive resources would sit idle, but the company still had to pay to maintain them. This “heavy lifting” was complex and inefficient.
Cloud computing, which became commercially available around 2006 or 2007, fundamentally changed this model. It is the delivery of computing services over the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis. Cloud providers handle the maintenance, security, and upgrades within their data centers, allowing users to access and configure resources remotely.
Core Characteristics of Cloud Computing
The cloud model is defined by several fundamental characteristics that provide its value:
High Availability (HA): Cloud computing architecture is built for resilience. It ensures a system is operational and accessible at any time , even if one component or server goes down.
Rapid Elasticity: Resources can automatically scale in response to changes in demand. When demand increases, more resources are added smoothly; when demand decreases, resources are reduced to save costs.
Measured Service: Cloud computing usage is measured, and users pay only for the resources they consume. This pay-as-you-go model eliminates the need for large, upfront capital expenditures.
- Resource Pooling and Virtualization: Cloud providers share resources like hardware, storage, and networking across multiple customers (a concept called multi-tenancy). The core technology enabling this is virtualization, which uses a hypervisor to divide physical hardware into virtual machines (VMs).
- Durability and Security: Cloud computing services offer durable storage, often replicating data to protect it. They also provide security controls that can exceed what is possible in a local data center.
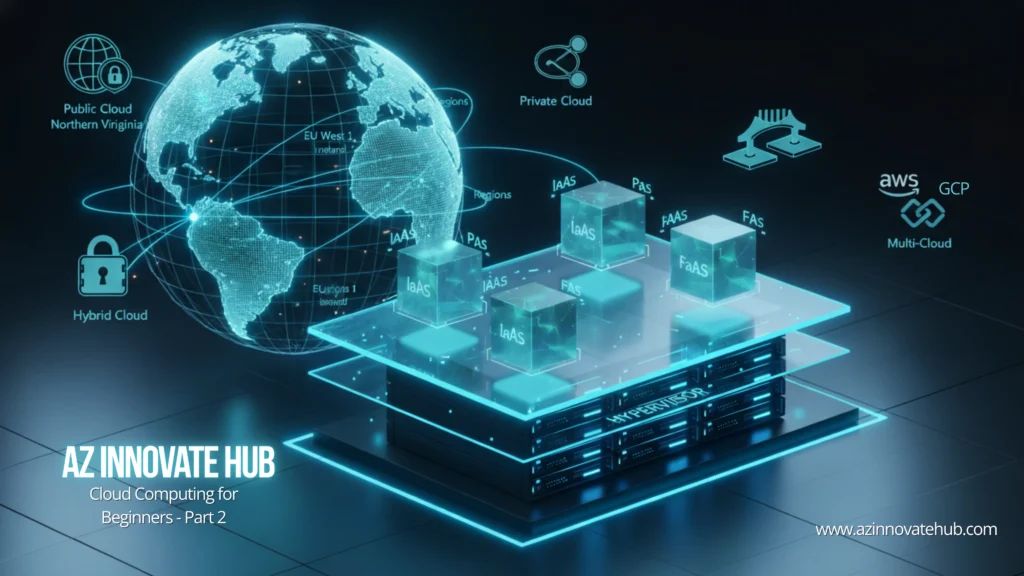
Cloud Computing Service Models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, and FaaS)
Cloud services are categorized by the degree of control the customer retains over the technical stack. This breakdown dictates the responsibilities shared between you and the cloud vendor.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
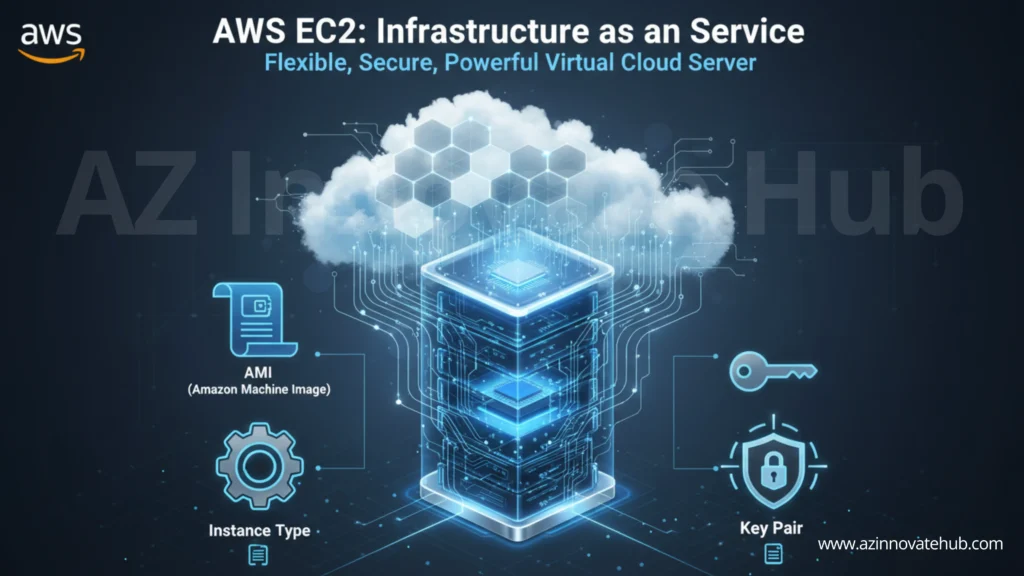
IaaS provides foundational computing resources over the internet. You essentially rent the basic building blocks, such as virtual servers (or virtual machines), storage, and networking components.
- Responsibility: The cloud provider manages the core infrastructure (storage, servers, networking). The user retains responsibility for the operating system (OS), middleware, application code, and data. This model offers the highest level of control and management from the consumer.
- Use Cases: IaaS is used for hosting applications, website hosting, and creating development and testing environments. AWS EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) is a primary example.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS delivers a ready-made platform that includes the operating system and development tools. It is designed to simplify application development and deployment.
- Responsibility: The provider manages the OS, virtualization, middleware, servers, storage, and networking. Developers only need to worry about their application code and data.
- Use Cases: PaaS is highly beneficial for developers building and deploying applications quickly, without the complexity of managing server environments. AWS Elastic Beanstalk is an example of a PaaS service.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS provides fully managed applications over the internet, ready for immediate use, and often accessed through a web browser.
- Responsibility: The provider manages the entire application stack, including the software, OS, and all underlying infrastructure. The user has no management responsibilities.
- Use Cases: Common examples include customer relationship management (CRM) software, email services (like Gmail), and office productivity tools
Function as a Service (FaaS) / Serverless Computing
FaaS is an event-driven execution model where your code runs in response to specific triggers. It is called “serverless” because the user does not provision or manage any servers.
- Responsibility: The provider handles all server provisioning, scaling, and management. The user provides only the execution code.
- Use Cases: FaaS is ideal for background tasks, processing data streams, and building microservices. AWS Lambda is a prominent FaaS example.
Cloud Computing Deployment Models
Deployment models define where the infrastructure resides and how it is accessed. The choice fundamentally affects security, scalability, and operational efficiency.
Public Cloud
Public cloud services are owned and operated by a third-party provider and shared among multiple organizations (tenants). The services are delivered over the public internet.
- Advantages: The provider manages all hardware and maintenance. It offers cost savings, high scalability, and eliminates large upfront capital expenditures.
- Disadvantages: Concerns exist about data privacy since resources are shared. Compliance requirements might prohibit using shared public servers for sensitive data. Performance can also be impacted by the speed of your internet connection.
- Examples: AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are the major public cloud providers.
Private Cloud
Private cloud infrastructure is dedicated to a single organization. It can be hosted on-premises or managed by a third party exclusively for that organization.
- Advantages: It provides a highly secure and customized environment with enhanced control. This is essential for organizations with strict security and compliance requirements, such as those in healthcare, finance, or government.
- Disadvantages: This model requires high expenses and significant management effort. Scaling often requires physically adding more hardware, which takes time and money.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid cloud combines two or more distinct computing environments, typically linking an on-premises data center (private cloud) with public cloud resources. The environments remain separate but are connected through secure links.
- Advantages: This model offers optimized cost by balancing capital and operational expenses. It allows organizations to control critical data on-premises while leveraging the scalability of the public cloud.
- Disadvantages: Managing connectivity and ensuring consistent security policies across different environments can be complex.
Community Cloud
This infrastructure is shared by organizations that have common concerns , such as specific compliance requirements, security needs, or mission goals. It allows organizations to collaborate and share costs while meeting regulatory standards.
Multi-Cloud Strategy
Multi-cloud involves intentionally using services from more than one cloud provider (e.g., using AWS for compute and GCP for data analytics). This strategy helps avoid vendor lock-in and allows businesses to leverage the unique strengths of different vendors.
Conclusion: Your First Step into the Cloud
Understanding “what is cloud computing” is the essential first step. You’ve learned how the pay-as-you-go model, rapid elasticity, and high availability of the cloud solve the problems of traditional IT.
We’ve defined the core service models—IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, and FaaS—which determine your level of control, and the deployment models, like public, private, and hybrid clouds, which determine where your infrastructure lives.
With this foundation, you are ready to explore the specific companies that provide these services. In the next article, we will compare the “Big Three” dominant cloud providers: AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).